Description
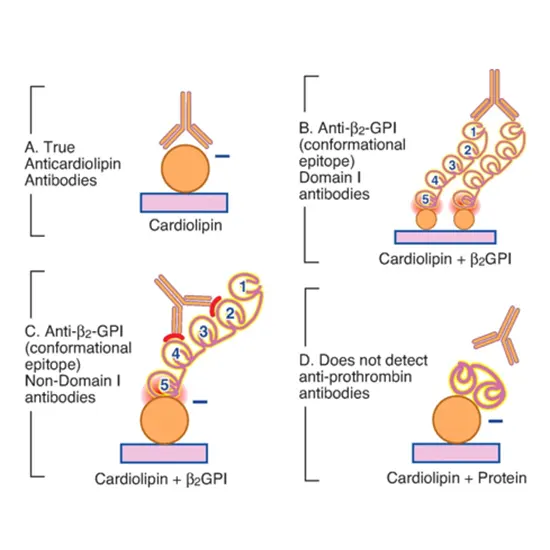
A cardiolipin antibodies panel measures the levels of immunoglobulin G (IgG), immunoglobulin A (IgA), and immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies directed against cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in the membranes of cells, including those in the heart.
Here’s an overview of each component and the significance of testing for cardiolipin antibodies:
- Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Cardiolipin Antibodies: IgG antibodies directed against cardiolipin are associated with antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), an autoimmune disorder characterized by abnormal blood clotting and an increased risk of thrombotic events (blood clots) in arteries and veins. IgG cardiolipin antibodies are one of the diagnostic criteria for APS and are linked to an increased risk of recurrent miscarriages, thrombosis, and other complications.
- Immunoglobulin A (IgA) Cardiolipin Antibodies: IgA antibodies against cardiolipin are less commonly measured than IgG and IgM antibodies. Elevated levels of IgA cardiolipin antibodies may also be associated with APS, but their clinical significance is not as well-established as that of IgG antibodies. IgA cardiolipin antibodies may be detected in some individuals with APS who are negative for IgG cardiolipin antibodies.
- Immunoglobulin M (IgM) Cardiolipin Antibodies: IgM antibodies directed against cardiolipin are also associated with APS. IgM cardiolipin antibodies may be the first antibodies to appear in the early stages of APS. They are often measured along with IgG antibodies in the diagnosis of APS.
The cardiolipin antibodies panel, which includes measurements of IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies, is typically used in the diagnosis and management of APS and other autoimmune disorders associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. A positive result for one or more of these antibodies, particularly IgG cardiolipin antibodies, in the appropriate clinical context may indicate an increased risk of thrombosis, pregnancy complications, or other manifestations of APS.
It’s important to interpret the results of cardiolipin antibody testing in conjunction with clinical findings and other laboratory tests to make an accurate diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment decisions. Treatment for APS often involves anticoagulant therapy to prevent blood clots and other complications.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.